Grenoble
Rhône
Alpes
Team
DRACULA
Current projects and Grants:
- BIMOD (head V. Volpert) 2010-2014, funded by ANR
- STOCHAGENE (head O. Gandrillon) 2011-2015, funded by ANR.
- Predivac, joint program with Inserm, Altrabio and Cosmo (Head J. Marvel at Inserm) 2013-2015, ANR (RPIB program)
- Modelling Leukemia (head T. Lepoutre), Inria Partnership program.
- Euromediterranean 3+3 "Mathematical Models and Methods in Cell Dynamics" 2012-2015
- Prion and Alzheimer (L. Pujo-Menjouet)
- Mathematical modelling of megakaryopoiesis and applications to platelet related diseases (French-Canadian grant for resarch)(L. Pujo-Menjouet)
- POLONIUM (L. Pujo-Menjouet)
Research themes
We are working on several applied directions related to hematopoieisis. Hematopoieisis is the scientific name used for blood formation. We especially focus on :- Normal hematopoieisis
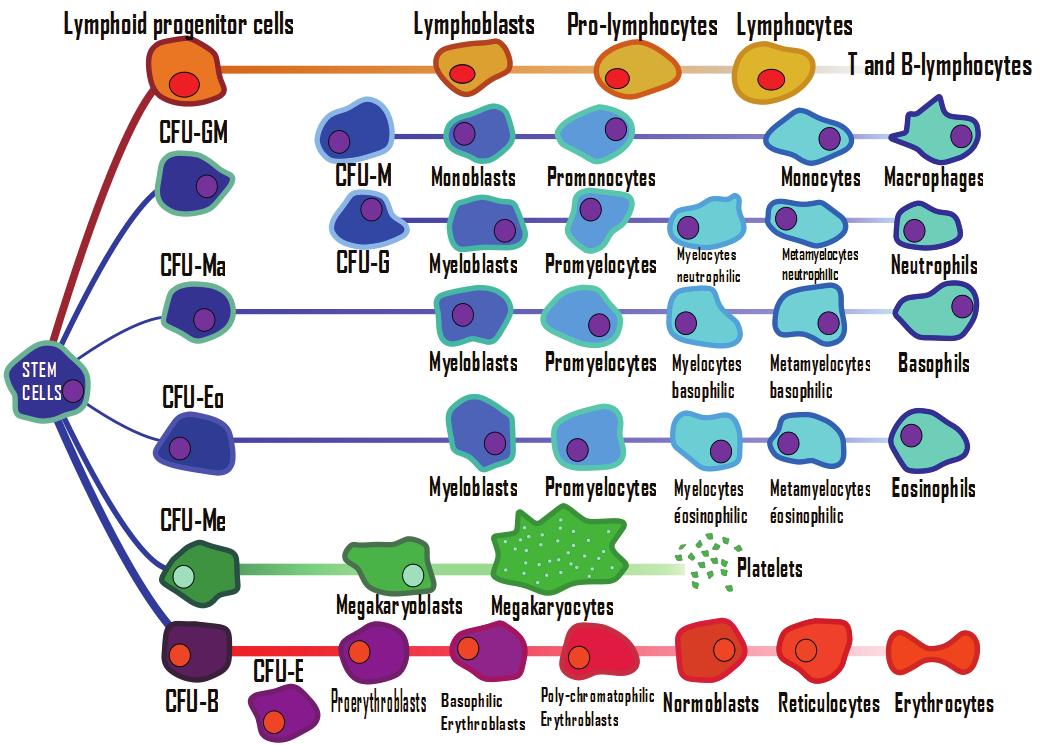 Hematopoiesis
is a complex process that
begins with primitive hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and results in
formation of mature cells: red blood cells,
white blood cells and platelets. Blood cells are produced in the bone
marrow, from where mature cells are released into the blood stream.
Modelling normal hematopoiesis will allow us to explore the dynamical
appearance of the various cell types, originating from the stem cell
compartment,
through the bone marrow development up to the blood stream.
Hematopoiesis
is a complex process that
begins with primitive hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) and results in
formation of mature cells: red blood cells,
white blood cells and platelets. Blood cells are produced in the bone
marrow, from where mature cells are released into the blood stream.
Modelling normal hematopoiesis will allow us to explore the dynamical
appearance of the various cell types, originating from the stem cell
compartment,
through the bone marrow development up to the blood stream. - Erythropoiesis
 The study of
the red blood cell
lineage will
involve
different scale levels, from the molecular one, with the effects of the
hormones on the surface and internal parts of the cell, and the red
branch population in its whole with all the interactions taken into
account.
In order to couple the cellular behaviour to explicit molecular events,
we will describe the events through a molecular network. Cellular
regulatory processes will be described through the use of nonlinear
ordinary differential systems. The complexity of the model we want to
analyze will appear through the nature of feedback loops that will
result in strong nonlinearities.
The study of
the red blood cell
lineage will
involve
different scale levels, from the molecular one, with the effects of the
hormones on the surface and internal parts of the cell, and the red
branch population in its whole with all the interactions taken into
account.
In order to couple the cellular behaviour to explicit molecular events,
we will describe the events through a molecular network. Cellular
regulatory processes will be described through the use of nonlinear
ordinary differential systems. The complexity of the model we want to
analyze will appear through the nature of feedback loops that will
result in strong nonlinearities. - Immune response
 The production of T-cells
during
an immune
response represents an
important activity of the lymphoid branch, part of leucopoiesis (white
blood cell production).
By considering molecular events leading to cell activation when
encountering a virus, we will propose a multi-scale model of the immune
response.
The production of T-cells
during
an immune
response represents an
important activity of the lymphoid branch, part of leucopoiesis (white
blood cell production).
By considering molecular events leading to cell activation when
encountering a virus, we will propose a multi-scale model of the immune
response. - Platelet lineage
Thrombopoiesis, the process of production and regulation of platelets, is similar to erythropoiesis although important differences are observed. These two processes have an immature progenitor (MEP) in common. Platelets are involved in blood coagulation, and can be the source of blood diseases (thrombopenia, thrombocytosis). Deterministic models, in the form of structured transport partial differential equations, will be proposed to describe platelet dynamics, through the description of HSC, megakaryocytic progenitor and megacaryocyte (platelet precursor) compartments.
- Pathological hematopoeisis
-
Hematopoiesis is a complex process which has a vital importance for the organism. Its malfunctioning can result in numerous blood diseases including leukemia (characterised by uncontrolled proliferation of blood cells). In the case of leukemia, the equilibrium between different cell types or between self-renewal, differentiation and apoptosis of certain cells can be violated. We will model development and dynamics of leukemia taking into account disequilibrium of regulatory networks or feedbacks.
- Treatment:
 We
are working on the modelling of
pharamcological treatments (in words: drugs). For instance,we study
chronotherapeutic treatment, where the time of administration is
considered as being very important.
We
are working on the modelling of
pharamcological treatments (in words: drugs). For instance,we study
chronotherapeutic treatment, where the time of administration is
considered as being very important. - Determining cell renewal
We have developed a mathematical method to estimate cell turnover in slowly renewing biological systems. Age distribution of DNA can be estimated from the integration of radiocarbon derived from nuclear bomb testing during 1955-1963. For slowly renewing tissues, this method provides a better estimate of the average age of the tissue than direct estimate from the bomb curve. Moreover, death, birth and turnover rates can be estimated.